As the ageing process begins, the structure of skin starts to change. These changes are reflected outwardly in texture and appearance.
Due to depleting levels of the natural substances that give skin its firm and youthful appearance, fine lines and wrinkles may appear. As the internal structure weakens further, a loss of skin volume or a loss of density may occur. Skin may also become more sensitive.
Signs & Symptoms
How to recognise sensitive ageing skin
Facial skin which is sensitive can have various signs and symptoms. It can be accompanied by itching, tightness or rashes.
Moreover, starting at the age of 25, the first signs of ageing become noticeable on the surface. Most visually apparent are fine lines and wrinkles, a loss of volume and a loss of density. However not all the changes can be seen. In the case of sensitive ageing skin, the most noticeable change is in the way the skin feels.
Skin ageing affects different skin layers
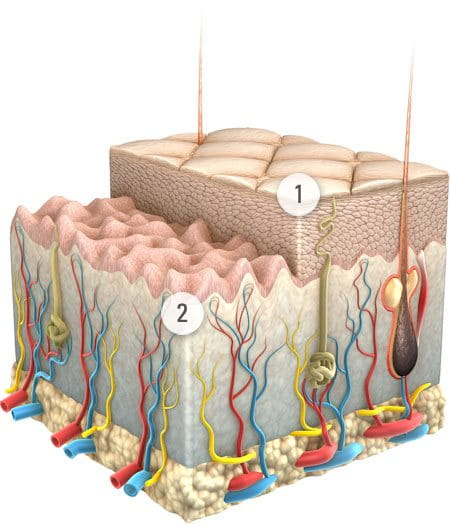

1. Epidermal layers
A slower cell turnover and reduction in lipid production on the skins surface means roughness and dryness are more likely. As this particular layer of the skin ages, it becomes more sensitive to UV light. The skin is less efficient at healing itself, and a reduction in immune function can lead to an increase in skin infections, together with slower wound healing. The skin may become less resilient and feel irritated more frequently.
2. Dermal layers
After the age of 25, there is a 1% annual decrease in collagen, one of the ‘building blocks’ of the skin. Together with a decline in elastin this leads to dermal tissue disorganisation. The structure of the skin is compromised and wrinkles are more likely. Elasticity is reduced, making the skin more prone to damage and broken capillaries. Reduced blood flow means a less efficient delivery of nutrition and oxygen to the surface.
How sensitive ageing skin looks and feels


The skin on the face is particularly thin and sensitive, which makes it more prone to damage and irritation from external factors. Natural, inevitable ageing processes result in a reduced capability for the skin to regulate moisture, regenerate and protect itself. This is the case when the skin’s barrier function is compromised and is exacerbated by naturally depleting levels of substances like Hyaluronic Acid, which hydrates the skin’s layers.
Skin that is sensitive and experiencing premature ageing can experience the following symptoms:
- Redness
- Dryness and a rough texture
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- A feeling of tightness
- Increased sensitivity to external factors
Causes & Triggers
What causes sensitive ageing skin?
Youthful skin contains natural substances at levels that keep it functioning well. As general skin ageing occurs, changes to the levels of these substances cause changes to the way it looks and feels. One of these substances, Coenzyme Q10, works to energise skin cells to improve their regenerative function so they are able to repair and rebuild themselves more efficiently.
A deficiency of Coenzyme Q10 leads to a reduced cell regeneration capacity, meaning skin becomes more susceptible to the damage caused by oxidative stress. This can lead to sensitive skin which shows signs of premature ageing such as fine lines and wrinkles and a dry surface texture.
Contributing Factors
What else affects sensitive ageing skin?
Aside from the inevitable ageing processes that occur within skin, including the decline in cellular energy as skin ages, there are a number of additional factors that can contribute to sensitive ageing skin.
Oxidative stress

Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the biological pathways that accelerate the skin ageing process. It occurs when certain lifestyle factors and exposure to specific substances result in the creation of free-radicals - volatile molecules that attack the internal cellular structure of skin, making it weaker and more likely to display visible signs of premature ageing such as wrinkles, a loss of volume and a loss of density.
Lifestyle factors which may contribute to oxidative stress may be:
Sun
Unprotected exposure to UV light is the primary cause of skin ageing. As well as accelerating the breakdown of collagen, which gives skin its structure, UV exposure can cause inflammation and sunburn, which may also make skin more sensitive.
Smoking
Nicotine and the toxic chemicals present in cigarettes affect the health of cells and make it harder for them to function efficiently.
Solutions
Tackling sensitive ageing skin
Key ingredients
As well as avoiding the outlined lifestyle factors, there is a number of active ingredients that have been proven to reduce the signs of sensitive, ageing skin.
- Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 is a substance found naturally in the body that helps cells convert nutrients into energy. Skin care products that include Coenzyme Q10 energise and strengthen cells and promote cellular regeneration.
Coenzyme Q10 is a powerful antioxidant. It helps skin to stay firmer for longer by giving it the ability to neutralise free-radicals caused by external environmental factors, such as UV and pollution. They contribute to the collagen and elastin breakdown responsible for the first signs of ageing such as fine lines and wrinkles.
- Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic Acid is a substance created within the skin. One of its key functions is to retain moisture and and it has the ability to bind in between 1,000 and 10,000 times its own weight in water (i.e. between one and ten litres). As we age, the skin's natural ability to produce Hyaluronic Acid depletes and wrinkles start to form and deepen. Products such as the Eucerin Hyaluron-Filler range that include Hyaluronic Acid may help to soothe the dryness often associated with sensitive, ageing skin.
- Ceramide-3
Ceramides are naturally present in the skin’s uppermost layers. They are a type of lipid that forms part of the skin’s essential barrier responsible for keeping moisture in and irritants out. In dry skin conditions, a deficiency of ceramides often exists. Including ceramides in skin care products may help to strengthen the skin’s barrier function, soothe skin dryness and prevent irritation.
Sensitive skin needs special care which should be highly tolerable and does not irritate skin. The Eucerin Q10 ACTIVE range shows good skin tolerability even on very sensitive skin and due to the Coenzyme Q10 has additional anti-ageing properties.
The Eucerin Q10 ACTIVE range contains Coenzyme Q10 and has proven to be effective at reducing the depth of wrinkles and firming ageing skin. It has been specially formulated for, and proven to be kind on, sensitive skin.
Skincare Routine

It’s important to treat sensitive ageing skin gently with a daily face care routine that won’t irritate or exacerbate any existing symptoms. Choosing mild cleansing products that are free of artificial colours and fragrance such as the Eucerin DermatoCLEAN range, may help to limit sensitivity.
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.